Voice Control with Dialogflow (api.ai) in a React-Native App

In the article “[The Potential of Voice Control](en/blog/33-das-potential-von-sprachsteuerung “The Potential of Voice Control)” we explained the importance of voice control. Now we want to address the technical side and explain how to develop voice controls using Api.ai. Api.ai has specialized in voice and chatbots since 2014 and has belonged to Google since 2016. With the technology offered, conversations between humans and machines can be designed and integrated into various services such as Alexa, Slack, Twitter, Facebook, and many more. Api.ai uses machine learning in the background to understand the exact intent of a voice or text input. This gives Api.ai an amazing interpretation accuracy and forms an ideal basis for business use cases as well.
Implementing a Use Case in Dialogflow (Api.ai)
For the first steps in Api.ai Dialogflow, such as creating a project or an “agent,” detailed documentation is offered. (https://api.ai/docs/getting-started/basics)
It gets really exciting when creating so-called “Intents.” An intent is essentially the definition of a function signature. When a voice or text command is sent from a user application to Api.ai, Api.ai uses its machine learning algorithms to find the appropriate signature and sends the function name and any associated parameters back to the user application. The user application can then execute the function and deliver the desired result to the user.
To illustrate the process, we take a shopping app as a use case, in which the user can view offers from different stores. The following screenshot shows what an intent can look like in Api.ai:!
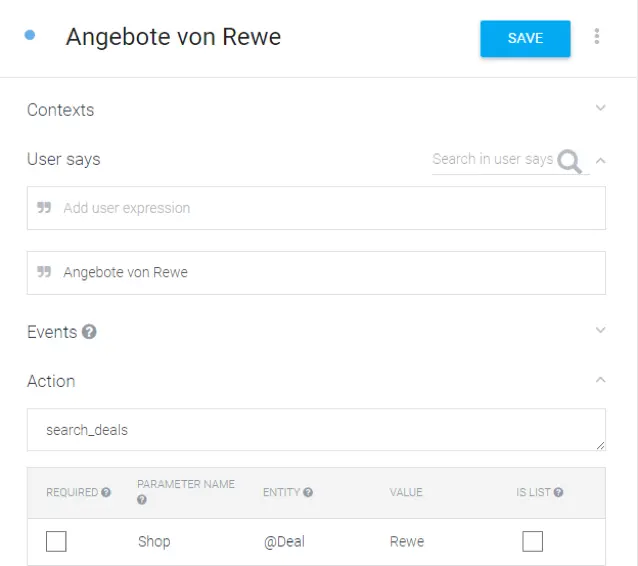
Dialogflow Example
The expected voice command is set to “Offers from Rewe,” where Rewe represents a parameter and is therefore variable. Through machine learning, Api.ai also understands related statements, such as “Deals from Rewe” or “Bargains at Rewe.” As a return, the associated function name (Action) “search_deals” with the parameter “Shop = Rewe” is returned.

API Function Call
ApiAi.setConfiguration(“4xxxxxxxe90xxxxxxxxc372”, ApiAi.LANG_GERMAN);
Besides English and German, many other languages are supported. A list can be found in our GitHub documentation: https://github.com/innFactory/react-native-api-ai#supported-languages Next, the voice command is recorded and directly processed with Api.ai with the simple call of “startListening”:
ApiAi.startListening(result=>, error=>);
Conclusion
With Api.ai, it is possible to develop professional voice controls. Our React-Native library “react-native-api-ai” provides easy integration for corresponding mobile apps.
 Anton Spöck
Anton Spöck


